Absolute Neutrophil Count Calculator
What is Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)
The Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) is a measure of the number of neutrophils in a person’s blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell (WBC) that plays a crucial role in the immune system’s response to infections, particularly bacterial infections.
The ANC is an important parameter used in assessing a person’s immune function, particularly in determining their risk of developing infections.
Normal Absolute Neutrophil Count
The normal range for Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the method used for measurement. However, generally, a normal ANC falls within the range of approximately 1,500 to 8,000 neutrophils per microliter (µL) of blood.
Usually reference range may vary slightly between different laboratories and may also depend on factors such as age, sex, and overall health status. ANC levels can fluctuate in response to various factors such as infection, inflammation, medications, and medical conditions.
Low Absolute Neutrophil Count
A low Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC), known as neutropenia, occurs when the number of neutrophils in the blood is below the normal range. Neutropenia can make individuals more susceptible to infections because neutrophils play a critical role in the body’s defense against bacteria and fungi.
The severity of neutropenia can vary, and it can be classified into three main categories based on the ANC:
- Mild Neutropenia: ANC between 1,000 and 1,500 cells/µL.
- Moderate Neutropenia: ANC between 500 and 1,000 cells/µL.
- Severe Neutropenia: ANC below 500 cells/µL.
Low Neutrophil Count Causes
Low ANC can be caused by various factors, including:
- Bone marrow disorders: Conditions such as aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, and leukemia can impair the production of neutrophils.
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy: These treatments can suppress bone marrow function and reduce neutrophil production.
- Medications: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics, antivirals, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause neutropenia as a side effect.
- Infections: Certain viral infections, such as HIV, hepatitis, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), can lead to neutropenia.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause the immune system to attack and destroy neutrophils. Source
How to calculate Absolute Neutrophil Count
The Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) is calculated using the following formula:
ANC = WBC × (Neutrophil % + Bands %) / 100
Where:
- ANC is the Absolute Neutrophil Count, measured in cells per microliter (µL) of blood.
- WBC is the White Blood Cell Count, also measured in cells per microliter (µL) of blood.
- Neutrophil % is the percentage of neutrophils among the total white blood cells.
- Bands % is the percentage of band neutrophils (immature neutrophils) among the total white blood cells.
To calculate the ANC:
- Determine the White Blood Cell Count (WBC) from a complete blood count (CBC) test result.
- Determine the percentages of neutrophils and band neutrophils from the differential white blood cell count, which is usually included in the CBC test report.
- Add the percentages of neutrophils and bands together.
- Multiply the total White Blood Cell Count (WBC) by the sum of the percentages of neutrophils and bands, divided by 100.
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) Example calculation
Question: Mr. James, a 45-year-old patient, recently had a complete blood count (CBC) test done. The results show a White Blood Cell Count (WBC) of 7000 cells/µL, Neutrophil Percentage of 58%, and Bands Percentage of 4%. Using this information, calculate Mr. James’s Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) in cells/µL.
Answer:
To calculate the Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC), we use the formula:
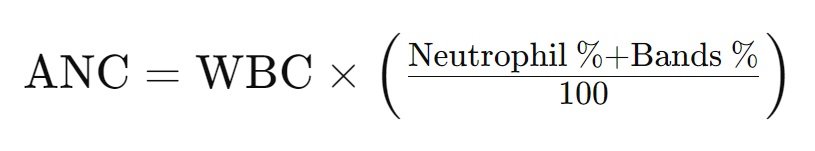
Given information:
- White Blood Cell Count (WBC) = 7000 cells/µL
- Neutrophil Percentage = 58%
- Bands Percentage = 4%
First, we need to find the sum of Neutrophil Percentage and Bands Percentage:
Neutrophil %+Bands %=58%+4%=62%
Now, we plug this value into the ANC formula:
ANC=7000×(62100)ANC=7000×(10062)
ANC=7000×0.62ANC=7000×0.62
ANC=4340 cells/µLANC=4340 cells/µL
So, Mr. James’s Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) is 4340 cells/µL.
Common Questions & Answers
How to increase absolute neutrophil count?
- Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients, including vitamins and minerals.
- Avoiding exposure to infections and practicing good hygiene.
- Managing stress levels and getting adequate rest.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Following a regular exercise routine, if approved by a healthcare provider.
- Discussing with a healthcare provider about any medications or treatments that may help increase neutrophil production.
What happens if absolute neutrophil count is low?
- Increased risk of infections, as neutrophils play a crucial role in fighting off bacterial and fungal infections.
- Fever, chills, and other symptoms of infection may occur more frequently and be more severe.
- Higher susceptibility to infections that may become severe or life-threatening if not treated promptly.
What if absolute neutrophil count is high?
- High ANC may indicate inflammation, infection, or other underlying medical conditions.
- It can be a sign of bacterial infections, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infections.
- In some cases, high ANC may occur temporarily in response to stress, exercise, or certain medications.
Absolute neutrophil count in pregnancy
- During pregnancy, ANC levels can vary, and they are generally higher than usual due to physiological changes in the body.
- However, ANC levels should still fall within the normal range established for non-pregnant individuals.
- Any significant deviations from the normal range should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying issues.
Average absolute neutrophil count.
- The average range for Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) is typically between 1500 to 8000 neutrophils per microliter (µL) of blood.
- However, the specific normal range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the method used for measurement.
What does absolute neutrophil count mean in a blood test?
- The Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) measures the number of neutrophils in a person’s blood.
- Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune response, particularly against bacterial and fungal infections.
- ANC levels are used to assess immune function and evaluate the risk of infections, especially in individuals undergoing chemotherapy or other treatments that may affect white blood cell production.
How can I lower my absolute neutrophil count?
- If ANC is high due to an underlying condition such as infection or inflammation, treating the underlying cause may help normalize ANC levels.
- In some cases, medications that suppress the immune system may be prescribed to lower ANC, but this should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider.